Aerial Mapping and Drone Survey LiDAR Products and Services
What is a Drone Survey?
A drone survey is a way of gathering data or information that makes use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), sometimes known as drones. Drones are outfitted with a variety of payloads like LiDAR and cameras that allow them to record 3D coordinates, images or video from the air. Aerial surveys are employed in a variety of industries, including agriculture, construction, land surveying, powerline inspection, wildlife habitat investigation, forestry, environmental monitoring, and many more. They have various advantages, including cost efficiency, safety, accuracy and environmental benefits, etc.
What is Aerial Mapping?
The process of making comprehensive maps and geographic information by gathering photos and data from an elevated position, generally from an aircraft or other flying platforms, is referred to as aerial mapping. This method is frequently used to collect data for a variety of applications such as land surveying, mapping, geographic information systems (GIS), environmental monitoring, and urban planning.
Why Choose LiDAR for Drone Surveying and Aerial Mapping?
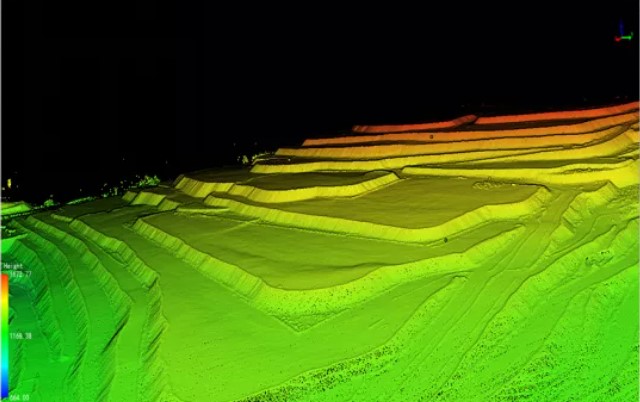
Aerial mapping and drone survey with LiDAR is a great way to map large areas and obtain accurate data sets. It offers the same results as traditional topographic surveys but with a faster turnaround time. This technology is also an effective alternative for aerial mapping of inaccessible or hazardous terrain.
The LiDAR aerial mapping technique uses laser light beams and on-board sensors, such as IMU and camera. Each reflected laser pulse is imaged on receivers, generating georeferenced point clouds which are then processed and used to generate three-dimensional models of the terrain, building, vegetation or any other assets. These 3D model can be analysed in GIS, AutoCAD or our own Point Cloud processing software such as LiDAR360, LiDAR360 MLS or LiPowerline.
LiDAR systems are used for aerial mapping and drone survey by industries such as construction, mining, agriculture and transportation. They provide dense, precise data and can work both day and night. Using these systems, businesses can quickly complete their surveying needs.
LiDAR is more accurate. When planning major assets, it’s important to have accurate information. If the data is not accurate, it can result in poor decisions, which can be expensive to undo. By utilising LiDAR systems, businesses can ensure that they have all the data they need to make the best possible decision.
In addition to producing accurate data, it can also provide fast data sets that can be integrated with other data sources. Compared to other types of aerial technologies, LiDAR has become more and more cost-effective nowadays.
Another benefit of using a LiDAR system is that it can map large, inaccessible terrain. LiDAR can also penetrate vegetation, making it an ideal solution for mapping areas of dense vegetation. With this kind of technology, it is also possible to map entire cities. Even though there are some limitations to using this technology, especially for finely detailed surfaces, this can be solved by adjusting the flight speed and overlap rate etc.
Using aerial mapping and drone survey technology makes it unnecessary to send any surveying technicians out into hazardous terrains such as rough wilderness, icy sites and locations with dangerous wildlife, all of which could potentially cause technicians to become injured. Using this technology to scan such areas eliminates these risks and creates a safer working environment.
Applications Of LiDAR Drone Surveying and Aerial Mapping
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) drone surveys record very precise 3D data, making them appropriate for a wide range of applications in a variety of industries. Here are some common applications for LiDAR drone surveys and mapping:
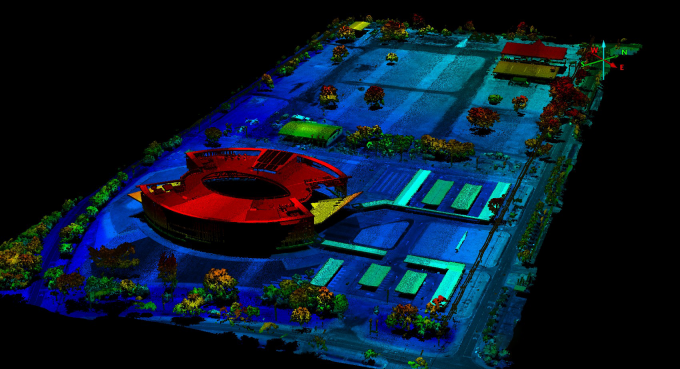
Topographic Mapping and Surveying:
- Creation of accurate digital elevation models (DEMs)
- Land surveying and boundary determination
- Terrain modelling for engineering and construction projects
Forestry and Vegetation Analysis:
- Assessment of forest structure and health
- Estimation of tree heights and canopy density
- Monitoring of vegetation changes over time
Urban Planning and Development:
- Detailed 3D mapping of urban areas
- Infrastructure planning and design
- Land use planning and zoning studies
Environmental Monitoring:
- River and watershed analysis
- Coastal erosion monitoring
- Land subsidence detection
Archaeology and Cultural Heritage:
- Identification of buried structures and archaeological features
- Preservation and study of cultural heritage sites
Mining and Quarrying:
- Volumetric measurements for stockpile management
- Geological mapping and exploration
- Safety assessments in mining operations
Floodplain Mapping and Hydrology:
- Modelling of floodplains and water flow
- Hydrological studies and flood risk analysis
Infrastructure Inspection and Maintenance:
- Assessment of bridges, roads, and buildings
- Detection of structural issues and maintenance needs
- Utility line inspection, including power lines and pipelines
Disaster Response and Recovery:
- Rapid assessment of disaster-affected areas
- Identification of damage and hazards
- Support for search and rescue operations
Precision Agriculture:
- Crop health assessment
- Soil and field analysis
- Yield prediction and management
Geological and Geophysical Surveys:
- Geological mapping
- Fault detection and seismic studies
- Ground subsidence and deformation analysis
Wildlife and Conservation:
- Habitat monitoring
- Wildlife tracking and population studies
- Biodiversity assessment
LiDAR drone surveys are especially useful in situations requiring high-precision 3D data, such as the examination of complicated terrains, forests or urban areas. These surveys give extensive and precise information for a variety of applications, resulting in better decision-making, better planning and increased safety in a variety of sectors.
LiDAR Drone Survey Solutions
What is the Best LiDAR Drone for Surveying and Mapping?
The “best” LiDAR drone for surveying can vary depending on your specific needs and budget. It’s essential to consider factors such as the survey area, required level of detail, budget and the type of LiDAR sensor that best suits your project.
Instead of asking which one is the best, the better question is “which one is the most suitable LiDAR drone for surveying”. That is why we are here to help our clients to find the right equipment and solutions for their surveying and mapping projects in terms of quality requirements and effective cost. You can leave the drone survey solution investigations to us, as this is how we bring the value to our customers.
Due to the weight of most aerial survey LiDAR system, ranging from 1kg to 3kg, the best drones that can suit LiDAR aerial mapping are DJI M210 RTK, M300 RTK, M350 RTK or M600. For the LiDAR payloads, there are options from entry level to premium LiDAR scanner for supreme accuracy.
Entry Level & Cost-Effective Drone LiDAR Payload
Mid & Premium Range LiDAR Payload
Large Scale Project Aerial LiDAR Survey Payloads
For a large scale aerial mapping or inspection job, the drone may not be the best, as it is not as fast as the helicopter or fixed-wing UAV. The airborne LiDAR scanner would be more cost effective and efficient, even if the cost for the payload and helicopter hiring is much more expensive than multi-rotor drones.
LiDAR Drone Survey and Aerial Mapping Software
We have one-stop solutions for processing the LiDAR aerial mapping point cloud data for industries like construction, forestry survey, powerline inspection, mining and agriculture, etc. With assistance from this mapping software, we are able to deliver reports and vector files like DEM and DSM to our customers.
-
LiDAR Point Cloud Processing Software
LiDAR360 MLS HD LiDAR Mapping Software – 1 Year Subscription
US$3,600.00 Excl. GST/VAT Add to basketRated 0 out of 5 -
LiDAR Point Cloud Processing Software
LiPowerline – Powerline Point Cloud Data Analyzing Software – 1 Year Subscription
US$3,600.00 Excl. GST/VAT Add to basketRated 0 out of 5 -
LiDAR Point Cloud Processing Software
LiDAR360 Point Cloud Data Management, Processing & Analyzing Software – 1 Year Subscription
US$3,600.00 Excl. GST/VAT Add to basketRated 0 out of 5
Why Choose LiDAR Solutions for LiDAR Drone Survey and Aerial Mapping?
Cost-Effective Pricing
By utilising a global supply chain, LiDAR Solutions can achieve the best pricing to accelerate the digitalisation of drone surveying and aerial mapping.
Projects Delivered with Good Quality and On-Time
We take pride in our commitment to delivering projects with exceptional quality and punctuality. Our dedicated team works diligently to ensure that each project is not only completed on time, but also meets the highest standards of quality and excellence.
FAQs About LiDAR Drone Surveying
What is the Cost of a LiDAR Drone Survey & Aerial Mapping?
The cost of a LiDAR drone survey can vary significantly based on a number of factors, including the exact project needs, the area to be surveyed, the level of detail required and the required deliverable. As a result, providing a precise cost without specific project specifics is difficult, however, we always give our client a lumpsum price with committed rates, guaranteeing there are no surprises during project execution.
The cost of a LiDAR drone survey is typically dictated by considerations such as:
- The size of the survey area – Larger regions take more time and resources, and we may need to utilise a helicopter survey LiDAR payload
- Resolution and detail – Generally, more resolution and greater detail in survey data results in higher expenses
- LiDAR technology – The cost can be affected by the type and quality of the LiDAR sensor utilised. High-end LiDAR sensors cost more but provide higher accuracy and detail
- Data processing – LiDAR data processing, such as filtering, categorisation and 3D modelling, can increase the final cost
- Survey aims – The survey’s unique aims, whether for topographic mapping, forestry analysis or another reason, can affect the cost
- Terrain and accessibility – The survey area’s terrain and accessibility may have an impact on expenses, especially if specialised equipment or approaches are necessary
- Regulatory and permitting fees – Permitting and compliance fees vary by area for some surveys
It is best to connect with our experts to receive an exact cost estimate for your LiDAR drone scan. We will assess the unique demands of your project, do a survey of the area and produce a precise cost estimate tailored to your specifications.
The cost of a LiDAR drone scan can range from a few thousand dollars for smaller, simpler projects to hundreds of thousands of dollars for large-scale, high-resolution surveys. To acquire an exact quote based on your individual project needs and financial limits, it’s critical to have a full discussion with our team.
What is the LiDAR Drone Survey Accuracy?
The accuracy of a LiDAR drone survey might vary based on various aspects, including the LiDAR sensor’s quality, flying parameters, ground control points employed and data processing procedures. LiDAR drone surveys may attain high levels of precision in general, and the achievable accuracy is usually expressed in terms of both horizontal and vertical accuracy.
Some common accuracy standards for LiDAR drone surveys are as follows:
- Vertical Accuracy – Vertical accuracy is a measure of how accurately LiDAR data matches genuine ground elevation. Vertical accuracy is often specified in terms of Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and can range from a few centimetres to tens of centimetres.
- Horizontal Accuracy – The horizontal accuracy of the LiDAR data indicates how closely it aligns with the genuine geographic position on the Earth’s surface. Horizontal accuracy can also be expressed in terms of root mean square error (RMSE) and is often comparable to or somewhat better than vertical accuracy.
It should be noted that achieving high accuracy in LiDAR drone scans may necessitate the following:
- The calibration and installation of the LiDAR sensor on the drone must be done correctly.
- Georeferencing requires precise GPS and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) data.
- A sufficient number of ground control points are required to accurately relate the LiDAR data to the ground.
- Flight planning and execution that reduces errors, such as maintaining constant altitude and overlapping flight lines.
- The achievable accuracy is also affected by the LiDAR sensor and drone system employed, with higher-end sensors and survey-grade equipment being more accurate.
LiDAR drone scans are well-known for producing very accurate and detailed 3D models of the scanned area. The accuracy requirements for a particular project may differ depending on the intended usage, and surveyors can modify their methods and equipment to match those needs. Working with seasoned individuals who can assess your specific project demands and assist you in achieving the necessary level of accuracy is critical.
What Deliverables Can LiDAR Drone Survey & Mapping Generate?
Depending on the exact project requirements and planned use of the survey data, LiDAR drone surveys can provide a variety of deliverables. The following are some typical deliverables related with LiDAR drone surveys:
- DEMs (Digital Elevation Models) are high-resolution, precise representations of the ground surface. Topographic mapping, land surveying and terrain analysis are all popular applications for DEMs.
- DSMs (Digital Surface Models): DSMs encompass not just the bare Earth’s surface, but also any things on it, such as flora, buildings and infrastructure. They are useful for urban planning, flood modelling and other purposes.
- DTMs are digital terrain models that portray the bare Earth with no above-ground features. They are required for engineering and land development projects.
- LiDAR surveys produce dense 3D point clouds that provide extensive information about the studied area. Point clouds are useful for a variety of applications, such as infrastructure inspection, cultural asset preservation and forestry study.
- Orthomosaics are high-resolution, georeferenced aerial images made by stitching together separate survey photographs. Its applications include visual examination, mapping and documentation.
- Contour maps are created by combining DEMs and DTMs to display elevation changes in a 2D manner. They are necessary in land development, engineering and site planning.
- Cross-sectional views show a profile of the terrain or features of interest along a specified line or path. These can be used to analyse infrastructure corridors and earthwork projects.
- Volumetric Calculations: LiDAR data can be used to compute material volumes, such as stockpile measurements in mining and building.
- LiDAR surveys may help create an inventory of assets such as utility poles, signs and plants, which is useful for maintenance and management.
- LiDAR data can be utilised for a variety of environmental investigations, including flood risk assessment, coastal erosion research and vegetation health monitoring.
- Building Information Models (BIM): LiDAR data may be used to produce accurate 3D models of buildings and infrastructure for architectural and engineering purposes using BIM software.
- LiDAR surveys can help assess damage and structural integrity following natural disasters or occurrences, assisting in recovery efforts.
- Customised Reports and Analyses: Surveyors can provide customised reports and analyses adapted to specific requirements, depending on the project’s objectives.
The selection of deliverables is determined by the project’s aims, and survey professionals will collaborate with customers to find the most appropriate outputs. These deliverables are useful for decision-making, planning, analysis and monitoring in a variety of industries, including construction and agriculture, as well as environmental management and cultural preservation.
Contact Us Today
If your organisation requires state-of-the-art drone survey and aerial mapping technology, LiDAR Solutions can provide a suitable solution. Call us today on 0412 752 033 or contact us online today to discuss your requirements.






